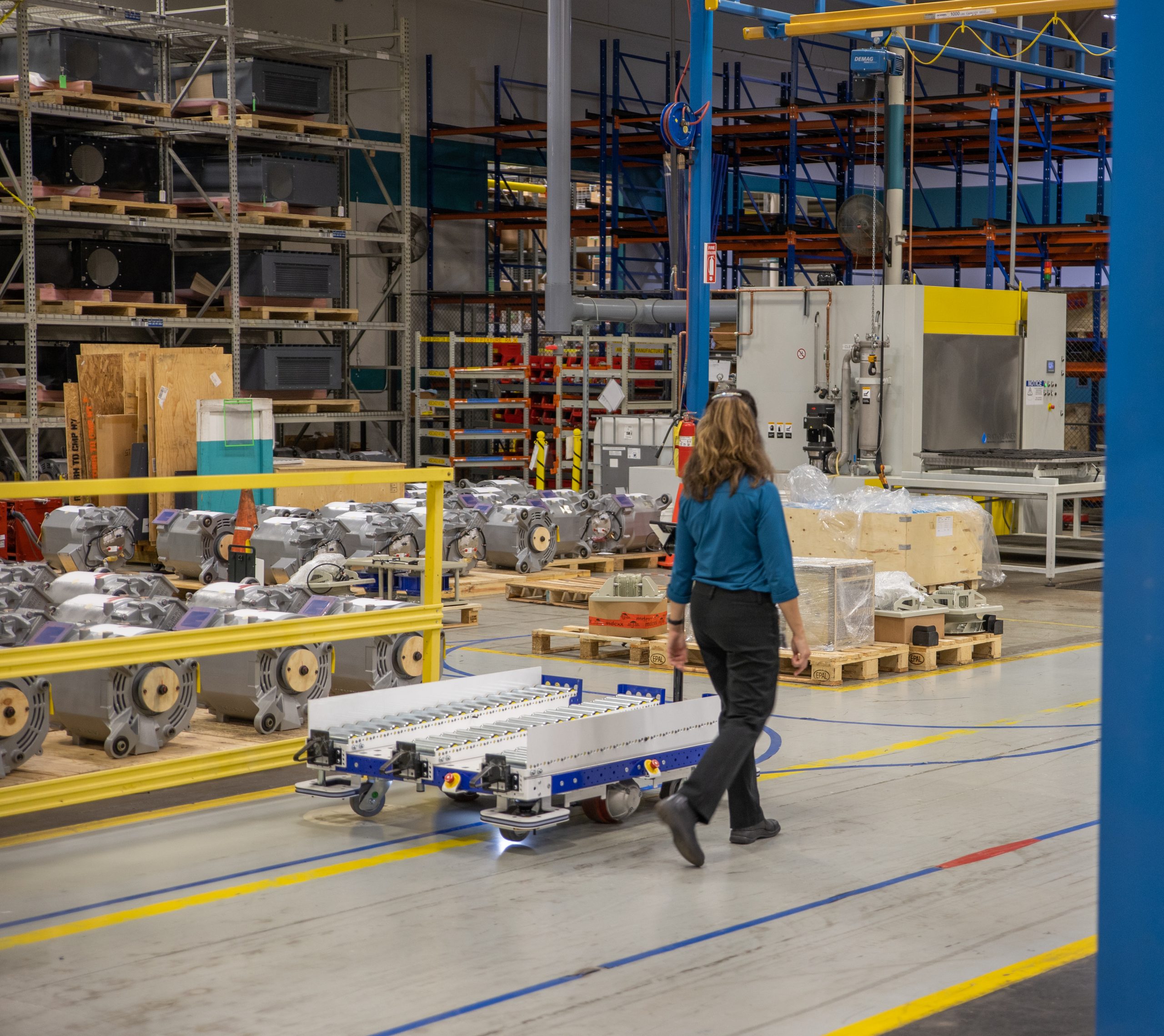
Making material handling safety a priority will improve the abysmal safety stats the manufacturing and warehousing industries currently have.
Discussions on technological advancement across the industrial sector are generally focused on operational efficiency while ignoring the safety of operators on facility floors.
Operational safety is also a key consideration for adopting transformative technologies such as industrial automation, which removes humans from dangerous situations.
The statistics also show that the traditional ways of protecting operators in industrial facilities need some enhancements. Conventional material handling systems such as forklifts and industrial trucks were responsible for approximately 85% of fatalities and 34,900 serious injuries in the United States. A cursory search of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration records will show that transportation equipment going off-track, inadequate loading equipment, and defective equipment were the major causes of these accidents.
The prevalence of accidents associated with material handling safety highlights the need to integrate operational safety tips within facilities. This post will explore some of the more important tips for optimizing material handling safety. These tips will take into consideration every operational process where errors can lead to dire consequences. Thus, tips will be categorized under operational safety tips, technological safety provisions and tips, and material handling equipment management.
Operational material handling safety tips
Building an optimized material handling system and ensuring it is properly operated is a blueprint manufacturing facilities and warehouses can employ to reduce safety-related incidents on facility floors. Stakeholders can improve operational safety by:
1. Optimize capacity and layout planning
The capacity of a facility and the state of its shop floor determine its productivity levels, as well as the level of safety that can be expected. A chaotic facility floor will experience traffic when transporting materials, and this is a recipe for disaster. Moving materials while operators zigzag through the pathways of industrial vehicles is also a recipe for disaster. Thus, proper planning is required.
Tip: Enhancing operational safety through proper capacity and layout planning is no longer a difficult process. Multiple digital transformation technologies such as simulation modeling software can be used to evaluate operational plans before implementation. A properly planned layout will include dedicated storage areas and pathways for transporting materials that are off limit to operators.
Implementation Responsibility: The responsibility for optimizing facility capacity and the layout that caters to material handling is that of C-level executives. Stakeholders must ensure safety features prominently within the context of improving operations or revenue. Stakeholders are expected to hire experts who can use the appropriate technology to develop optimized plans.
2. Implement a safety culture
The culture of ‘profitability no matter what happens’ has negatively impacted the implementation of safety within the industrial sector. Putting finances first sends a message across to operators, and that message is ‘we do not really care about your safety, just get the job done’.
Implementing a safety first tradition in place puts the rank and file on the side of management and motivates employees to do their best. The LyondellBasell story is an excellent example of how this works. To stave off bankruptcy, the plastics and chemicals refining company hired Jim Gallogly as its CEO. In his first meeting, the new CEO outlined his commitment to safety before discussing the dire financial situation the company found itself in. The focus on safety reduced shop floor accidents, motivated employees, and increased productivity.
Tip: Implementing a safety-first initiative reduces an enterprise’s risk of financial loss from safety-related incidents. Safety policies should include developing strategies to deliver material handling safety within a facility.
Implementation Responsibility: Managers are expected to draft safety policies and implement them through the training of shop floor operators. Providing incentives for departments that adhere to safety policies also incentivizes others to follow through.
3. Welcome regulators as consultants
The boys in suits or the boys from the government are generally seen as nuisances who make life difficult for operators. Many operators and managers also believe regulators have no skin in the game and do not understand operational dynamics…but this is far from the truth.
Regulators are also affected by increasing accident rates as their names are attached to the facilities they visit. Thus, regulators should be welcomed just like the expensive operational consultants you pay a premium to for productivity-related advice.
Tip: The tip is in the title. View regulators from the government as cheap consultants and ensure the recommendations they provide are implemented.
Implementation Responsibility: The responsibility of welcoming regulators falls on the shoulders of facility managers and supervisors who work directly with operators and order pickers using material handling systems.
implementing technological
solutions tips: The digital transformation of the industrial sector supports the application of automated solutions to ease the operational challenges operators face. Some tech-related tips to ensure material handling safety include:
4. Automate the material handling process
Removing humans from the material handling process drastically reduces material transportation-related accidents. Currently, two automation solutions that you can use exist. These are autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) and automated mobile robots (AMRs). AGVs reduce accidents because they have dedicated tracks that do not cross operator pathways, and they can be controlled using wearables when they go off-track. AMRs navigate the shop floor using collision-detection technology that ensures they function at safe speeds and navigate the floor without colliding with objects.
Tip: Industrial automation reduces the possibility of human error when material handling systems are in operation. This reduces accidents and ensures facilities are safer for human operators.
Implementation Responsibility: Project managers and C-level managers are expected to analyze the viability of an automated material handling system to pursue their implementation.
5. Employ remote monitoring
The need for supervisors who move from station to station to ensure materials get to specified locations on time has become obsolete. Remote monitoring technology solutions such as IoT and tracking sensors can easily pinpoint the location of material handling equipment and the speed they are moving without putting a human in harm’s way. Remote monitoring solutions are subsets of Industry 4.0 as they leverage the interexchange of data within facilities and data analysis to calculate risk factors. Understanding the risk factors associated with material handling equipment in real-time reduces accidents.
Tip: Monitoring material handling systems ensure that materials are properly handled and transported within specified speed limits within a facility. Thus, when transporting heavy-duty materials, supervisors can easily manage transportation speeds to eliminate safety incidents.
Implementation Responsibility: Stakeholders that decide the utilization of technological solutions within the shop floor are responsible for implementing remote monitoring strategies. Individual safety officers must also be trained to monitor material handling systems to prevent accidents.
6. Integrate safety implementation technologies
In certain scenarios, even automated guided vehicles can go off-track. When this occurs, there must be fail-safe solutions to ensure off-track AGVs can be controlled and brought to a stop without harming workers on the shop floor. Technologies such as wearables provide operators with a means to control errant vehicles to safety without being in their path.
Tip: Implement fail-safe solutions to ensure material handling equipment does not cause damage when they go off-track. Technologies such as wearables and IoT devices can help with controlling off-track AGVs.
Implementation Responsibility: Implementing safety measures is the responsibility of project managers, while operators must be trained to utilize safety implementation technologies when incidents occur.
Tips for proper material handling equipment management: The equipment used to transport materials across the shop floor must be properly managed to forestall accidents and deliver increased productivity. To achieve this, operators must understand the proper processes of handling material handling equipment and taking care of them. The tips provided here can help with proper material handling equipment management.
7. Devise predictive maintenance strategies
Industry 4.0 focuses on leveraging historical data to prevent downtime, which can be caused by faulty material handling equipment. Implementing a predictive maintenance strategy ensures faults are easily discovered and mitigated in real-time to forestall unplanned downtime. Predictive maintenance also reduces the possibility of material handling equipment developing a defect while in operation. Unforeseen faults or defects can lead to accidents within the facility.
Tip: Ensure predictive maintenance strategies are developed from accurate data analysis with the capacity to accurately predict the need for future maintenance and repairs.
Implementation Responsibility: Stakeholders are tasked with devising predictive maintenance strategies while repair technicians handle the repair and maintenance activity.
8. Train staff on proper material handling
Achieving material handling safety starts with training the employees who utilize manual material handling equipment on proper utilization. Continuous training ensures employees do not make common errors such as running with carts to speed up delivery or pulling a cart from the front instead of pushing. Properly trained staff are more likely to avoid the errors that lead to accidents on the shop floor.
Tip: Outsource staff training to material handling system experts who understand what it takes to properly operate a cart.
Implementation Responsibility: The training and validation required to ensure material handling safety must be initiated by stakeholders, while the training process should be handled by professionals.
9. Secure transportation routes
Securing the routes material handling equipment takes when making deliveries or picking orders to improve material handling safety. Securing these routes means ensuring obstacles do not obstruct pathways and the floors are properly graded and built to support the movement of equipment. The floor should also be properly maintained to ensure snags, holes, and other defects do not get material handling equipment to go off-track.
Tip: Implement a route maintenance policy to ensure transportation pathways are always at their optimal condition.
Implementation Responsibility: Floor managers and supervisors are tasked with inspecting material handling systems to ensure the pathways are secure.
10. Sustained vigilance
Implementing every strategy to improve material handling safety without consistently applying these measures reduces their efficiency levels. Sustained vigilance and training and retraining employees are the recommended solution to delivering lasting safety within the shop floor.
Tip: Managers must consistently schedule training to ensure everyone remains on their toes where upholding safety measures are required.
Implementation Responsibility: Everyone that works within a facility and has cause to navigate the shop floor must be responsible for upholding implemented safety strategies.
Conclusion
Corporate leaders in the industrial sector must reassess what safety means and the importance of material handling safety to deliver sustainable, accident-free environments. Making safety a priority is guaranteed to improve the abysmal safety statistics the manufacturing and warehousing industries currently experience.