Quality management goals are beneficial for driving success, customer satisfaction, and sustainability in all facets of manufacturing. Defining and incorporating these goals into existing work practices and policies sets the base for the company to drive continuous improvement and create value for its products and services. Companies that implement a quality management system (QMS) can easily streamline people and process management, increasing productivity and encouraging innovation among employees and stakeholders for maximum returns on investment.
Quality management goals define priorities and strategies manufacturers should adopt to achieve specific milestones or business outcomes. Refining these goals helps companies to standardize quality management systems and formulate efficient procedures, policies, and team functions. Setting SMART quality objectives is the first step in implementing Quality management goals:
- Specific- clearly defined
- Measurable – how much will the goals impact operations?
- Attainable – the company should have the capacity to implement and meet the QMS goals
- Realistic – the goals should be relevant and aligned with the company’s strategic plan
- Time-specific – all goals should be time-bound
Establishing quality management systems for manufacturing facilities should adhere to several principles for easy implementation and increase their success rates. The system should focus on continuous quality improvement, people engagement, data-driven decision-making, customer focus, the process approach, and managing relationships with stakeholders.
Quality management goals are bound to change with time. Sometimes, manufacturers rely on outdated quality policies, leaving them uncompetitive. What should manufacturers do to expedite the achievement of quality management goals and enhance their success rates?
Quality programs demand frequent facility audits and inspections
Process, personnel, and equipment inefficiencies can cause defects and non-conformities that lower product quality. Some inefficiencies can remain undetected – unless the manufacturer establishes a rigorous facility audit and inspection program. Audits can unearth ineffective quality management processes, non-productive work, and staffing inadequacies.
Manufacturers should also inspect all production assets to ensure they are in perfect working conditions and avert frequent breakdowns. It also helps the management to establish and implement a reliable factory maintenance program that optimizes asset availability and effectiveness. Regular facility inspections are vital for identifying maintenance challenges and defects that lower asset efficiency, leading to low-quality products and frequent and extended production downtime.
Manufacturers can conduct facility audits and inspections using manual and automated systems. The supervisory team can analyze past production records to evaluate historical quality patterns. They also scrutinize equipment maintenance data stored in Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) to quantify the effectiveness of existing maintenance strategies and their contribution to continuous quality improvements.
Manufacturers should leverage QMS documentation policies to record and communicate findings among employees and stakeholders. The results from these audits are crucial for validating manufacturing processes and tweaking their efficiencies to match production needs. Manufacturers rely on audit data to develop short and long-term inspection schedules to monitor compliance among employees and stakeholders.
Achieve quality management goals faster with a leadership team
Manufacturers can achieve quality management goals by appointing a leadership team to spearhead the implementation of new work practices and quality improvement procedures. The leadership team focuses on creating a uniform work culture across the facility, inspecting compliance, and identifying potential bottlenecks. Introducing a quality management system in a facility disrupts existing work practices, and such changes may not sit well with some employees. The leadership team is responsible for communicating these changes and their impact on workflows and product qualities.
The leadership team also identifies and rewards employees that immensely contribute to achieving quality management goals. These are employees that comply with existing quality policies, help other employees to adopt new work practices, and leverage innovative work practices to enhance continuous improvement.
The leadership team frequently updates policies and objectives once the team achieves particular milestones. The leadership team helps employees to develop a sense of responsibility and dedicate their skills and time toward achieving quality management goals. They review inspection reports and make necessary recommendations to the senior management to ensure the objectives are achieved.
Companies should choose the leadership team from the existing workforce. The team should comprise individuals with extensive knowledge of the company’s work practices. They should be proactive and possess a positive attitude toward changing work schedules and culture.
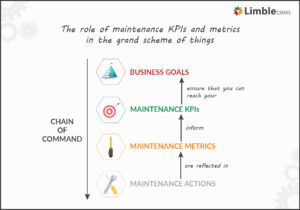
Tracking performance reduces quality mistakes
When defining quality management goals, manufacturers specify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure and track the success of the quality management system. Performance indicators keep the entire team focused on achieving quality management goals. They assist all teams across the facility to streamline workflows and reduce mistakes that can impede the quality of products and the efficiency of processes.
Manufacturers should track the performance of different teams and individual employees and how far the entire company is toward meeting its quality goals. The indicators are vital for identifying mistakes and errors in routine workflows and help the company to decide on appropriate improvement measures to correct and eliminate them.
KPIs are bound to change as the company achieves several quality management goals. Manufacturers should set KPIs targeting all facets of the production facility. Therefore, the KPIs should address employee management, production scheduling, maintenance strategies, and external collaborations. The company should standardize the tracking and reporting of key achievements and subsequent work strategies to enhance performance, product quality, and customer satisfaction.
Training employees is critical for meeting quality management goals
Quality improvement in manufacturing comes with technological, procedural, and policy changes that transform how people and machinery work. These changes can affect employee productivity since some may struggle to understand how some tools and technologies work. Manufacturers should provide adequate training to employees to acquaint them with new policies, management strategies, and the utilization of quality management tools.
Training schedules and frequency should align with the changing quality management goals. The company explains the relevance of these goals on productivity, employee wellness, company competitiveness, and the need to comply with internationally-approved quality standards. The training exposes employees to additional work tools and standards applied when documenting daily production and reporting defects and quality issues.
Training helps employees to develop a continuous improvement culture and foster teamwork with a focus on enhanced product quality. The training period equips employees with the knowledge to identify process and product quality issues and ways to reduce them. It keeps employees engaged and focused on achieving and surpassing quality management goals in time.
Acquiring accreditation symbolizes compliance with industry standards.
When setting quality management goals, companies should aspire to acquire international standards. These standards have principles and quality management provisions that can enhance a company’s compliance with industry regulations and the quality of manufactured products. Companies can work towards achieving the ISO 9001 quality management standard or other accreditations relevant to their sector.
Acquiring and implementing these standards helps companies to standardize work practices, improve the consistency of production processes and expedite the realization of quality management goals.
Summing Up
Achieving quality management goals is a lengthy process that demands multiple changes across the facility. The workforce encounters new policies, practices, and tools that can disrupt the usual routines. The entire process requires goodwill from all levels of the company and the allocation of financial resources to facilitate training and investment in complementary work tools. Manufacturers should establish measures to track performance, foster continuous improvement and update quality management goals as the company expands.
About the Author
Bryan Christiansen is the founder and CEO of Limble CMMS. Limble is a modern, easy-to-use mobile CMMS software that takes the stress and chaos out of maintenance by helping managers organize, automate, and streamline their maintenance operations.